

















September 2025
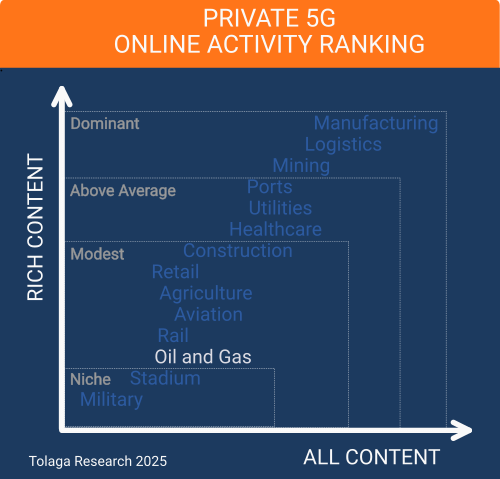
The oil and gas industry has a modest impact on the Private 5G (P5G) market, with our online content survey ranking it 12th out of the 14 industries researched.
Nokia and Ericsson lead P5G narrative in oil and gas, with solutions to enhance safety, efficiency, and automation across offshore platforms, refineries, and pipelines.
The oil and gas industry is at a crossroads. Major oil and gas companies are facing pressure to decarbonize while maintaining their core operations profitably.
Digital transformation is essential. Technologies like AI, digital twins, IIoT, and edge computing are central to operational optimization and ESG compliance.
P5G as an enabler. P5G supports real-time monitoring, automation, predictive maintenance, and remote operations—especially in hazardous environments.
Modest P5G adoption shows promise. Companies such as ADNOC, PETRONAS, Aramco, and Aker BP are leading with P5G deployments that demonstrate tangible operational and economic benefits.
But adoption barriers persist. High costs, integration complexity, spectrum challenges, and unclear ROI limit broader adoption, especially for firms with lower digital maturity or competing priorities.
The path forward. A targeted, phased approach focused on high-impact use cases and cross-industry collaboration is essential. Demonstrating value through pilots is key to scaling.
The outlook. P5G shows potential, but widespread adoption will depend on overcoming persistent challenges and proving its value in critical applications.
The global oil and gas industry in 2025 remains dominated by state-owned and multinational giants, with Saudi Aramco leading by a wide margin in market capitalization at $1.56 trillion, followed by ExxonMobil ($473 billion) and Chevron ($250 billion). Other major players include PetroChina, Shell, TotalEnergies, ConocoPhillips, CNOOC, and emerging regional firms like TAQA in the UAE. As the energy transition accelerates, these companies face a strategic crossroads, investing cautiously in decarbonization and alternative energy while maintaining core hydrocarbon operations.
Upstream investment is expected to decline modestly, particularly in US shale, reflecting tighter capital discipline and a shift toward optimizing existing assets over aggressive expansion. Geopolitical tensions, regulatory shifts, and continued consolidation, particularly in regions such as the Permian Basin in West Texas and Southeast New Mexico, are reshaping competitive dynamics. Meanwhile, technological innovation and digital transformation continue to enhance operational efficiency.
Despite growing pressure to reduce emissions and diversify, global oil demand is still projected to increase in 2025, supporting the financial strength of the industry’s most prominent players as they navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain future.
Digital transformation in the oil and gas industry focuses on enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and sustainability through the use of advanced technologies. Key strategies include deploying AI and data analytics for predictive maintenance and production optimization, leveraging digital twins for real-time asset monitoring, and using IIoT sensors for remote operations. Cloud computing and edge processing support scalable, low-latency data management, while automation and robotics reduce costs and improve safety. Cybersecurity is a growing focus, especially as IT and OT systems converge. Companies are also digitizing their supply chains, utilizing blockchain for enhanced traceability and smart procurement. To meet sustainability goals, firms are adopting digital tools for emissions tracking and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting. At the same time, AR/VR and mobile platforms enable remote collaboration and workforce training.
Online content published since 2022 that related to P5G for the oil and gas industry was collected and filtered using proprietary web crawling, AI, and NLP tools, yielding a corpus of 123 relevant impressions (ALL CONTENT). Of this, 98 focused on company activity in the sector (RICH CONTENT), identifying 84 companies. Approximately 30.0% of the content in the corpus referenced multiple industry verticals in addition to oil and gas, with an average of 2 to 3 other industries mentioned in this content.
The chart below compares the content corpus for P5G for the oil and gas industry against other industry verticals to gauge relative market momentum. The analysis indicates that oil and gas is currently a modest vertical market segment for P5G.
Natural language processing (NLP) and AI tools were used to identify companies mentioned in the content corpus, measure their prevalence (BREADTH), and evaluate how frequently they appear alongside other companies (DEPTH). For the 84 companies identified, the ranking of the top 10 is shown in the chart below.
Nokia is advancing P5G in the oil and gas industry by deploying secure, high-performance wireless networks designed for harsh and remote environments. Its solutions, such as Modular Private Wireless and Digital Automation Cloud, support real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, automation, and mission-critical communications across offshore platforms, refineries, and pipelines. Nokia’s technology enhances operational safety, efficiency, and resilience while enabling digital transformation and seamless edge computing for oil and gas companies worldwide.
Similarly, Ericsson is deploying P5G networks in the oil and gas industry to provide secure, high-speed, and low-latency connectivity tailored for challenging environments, such as offshore rigs and refineries. Their solutions support advanced use cases, including connected worker programs, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, autonomous robots, and enhanced safety through video analytics. These private networks enable seamless communication and data exchange, driving operational efficiency, reducing downtime, and improving safety across the oil and gas value chain.
NLP and AI techniques were used to identify and classify keywords and phrases in the content corpus into 25 topics. Their frequency was measured (BREADTH) and their inter-relationships analyzed (DEPTH). The chart below shows the top 10 topics.
The most prominent topics in online content today are compute and communications, security, remote operations, and digital oilfields. Over time, we expect themes such as artificial intelligence, regulations, and compliance to increase in prominence.
P5G is a key enabler of digital transformation in the oil and gas industry, particularly in supporting the shift toward autonomous operations, data-driven decision-making, and low-carbon initiatives. Some notable examples of how the industry is using P5G are summarized below.
ADNOC is the state-owned, fully integrated energy major of Abu Dhabi, responsible for the exploration, production, refining, and distribution of oil and gas. In July 2024, ADNOC announced a significant initiative to deploy an extensive private 5G (P5G) network in partnership with e&, covering 4200 square miles across its onshore and offshore operations. The network will connect more than 12,000 sensors in wells and pipelines, enabling real-time data transmission, AI-driven automation, predictive analytics, and autonomous control room operations. This deployment is designed to reduce costs, enhance operational efficiency, lower emissions, and improve workforce safety. ADNOC expects the initiative will generate $1.5 billion in economic value over five years.
In June 2024, Aramco Digital, a subsidiary of Saudi Aramco, was awarded access to the 450 MHz radio spectrum, which it intends to use to deploy a dedicated nationwide industrial 5G network. While Aramco Digital aims to offer its network services to a wide range of industries in Saudi Arabia through its Nawat marketplace, it is expected that Saudi Aramco will leverage the network to advance its digital transformation initiatives, focusing on enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and sustainability across its extensive and complex operations.
In March 2025, Ericsson and Ooredoo Qatar signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to accelerate digital transformation across Qatar’s oil and gas industry and other key sectors through the development of private and dedicated 5G network solutions tailored to industrial needs. The MoU focuses on co-developing mission-critical, high-performance 5G networks using Ericsson’s dual-mode core and advanced radio technologies, enabling secure, reliable, and high-speed connectivity in both offshore and onshore environments. The partnership will explore advanced use cases such as autonomous operations, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven optimization, while also supporting sustainability efforts to decarbonize operations and advance Qatar’s Net Zero ambitions. The collaboration aims to pave the way for future integration of 5G-Advanced capabilities, ensuring continued innovation and enhanced network performance for the oil and gas sector.
Centrica Storage, a UK energy company, operates major gas storage and terminal facilities in East Yorkshire and is actively developing hydrogen infrastructure. The company has deployed P5G at its Easington gas terminal in partnership with Vodafone Business, utilizing Ericsson equipment to replace legacy Wi-Fi systems across both indoor and outdoor areas. The new network enables near-real-time detection of equipment faults and gas leaks, allowing for rapid maintenance responses and significantly improving both personnel and environmental safety. The integration of IoT sensors and augmented reality tools further enhances remote diagnostics and inspections, streamlining operations and reducing unplanned downtime. For Centrica Storage, P5G offers a compelling value proposition by strengthening worker safety, improving operational continuity, lowering costs, and advancing its digital transformation agenda.
Aker BP is a leading Norwegian oil and gas company engaged in exploration, field development, and production across the Norwegian Continental Shelf.
In May 2025, Aker BP announced a proof-of-concept (POC) deployment of a P5G network with mission-critical push-to-talk and edge computing capabilities at its Edvard Grieg offshore platform, described as the world’s first fully autonomous P5G installation on an offshore production facility. The trial was delivered in collaboration with Tampnet, which deployed the private 5G and edge compute infrastructure, and Leonardo, which supplied the mission-critical push-to-talk (MCX) system.
Following the successful trial, Aker BP confirmed in July 2025 the full-scale deployment of private 5G at Edvard Grieg and announced plans to extend the solution to six additional North Sea platforms, in partnership with Mavenir and Tampnet. The network is intended to support a range of advanced use cases, including mission-critical communications, IoT, autonomous drones, robotics, and digital twins.
The PCK Refinery in Schwedt, Germany, is a significant oil processing facility with a capacity of approximately 11.6 million tonnes per year, primarily refining Russian Ural crude via the Druzhba pipeline and supplying 95% of the Berlin and Brandenburg regions’ auto fuels, as well as producing diesel, jet fuel, heating oil, and other petrochemical products. The refinery deployed its private 5G network in October 2022, covering 5 square miles to deliver ultra-reliable connectivity and communications for over 3,000 employees.
Changqing Petrochemical launched a P5G network in June 2021 at its refining facility in Xianyang, Shaanxi Province, in partnership with Huawei and China Telecom. The network supports a range of advanced use cases, including real-time remote inspections using high-definition video and 3D digital platforms, predictive maintenance through continuous monitoring of critical systems to reduce equipment failure, and process optimization enabled by seamless data exchange and AI integration across sensors and control systems. It also enhances safety and environmental performance by allowing real-time monitoring of operations and emissions, while high-performance edge computing strengthens data security and supports faster decision-making.
PETRONAS is Malaysia’s national, fully integrated oil and gas company, with global exploration, production, and energy operations. In August 2024, PETRONAS launched a P5G network at its Bintulu LNG Complex in Sarawak, the world’s largest LNG facility. The deployment, carried out in collaboration with Telekom Malaysia (TM) and Digital Nasional Berhad (DNB), is part of PETRONAS’s broader digital transformation strategy. It builds on earlier 5G initiatives at four other sites, including the Regasification Terminal Sungai Udang (RGTSU) in Melaka, where 5G was first introduced in 2022. The P5G networks support real-time monitoring, industrial IoT, AI-driven analytics, drones, robotics, and automation, significantly enhancing operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, workforce safety, and decision making. This connectivity is especially valuable in managing complex industrial processes within hazardous environments.
OQ Technology has successfully deployed its proprietary global 5G Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Low Earth Orbit satellite constellation, delivering secure, satellite-based non-terrestrial network (NTN) connectivity specifically for industrial use cases, including oil and gas. Their technology has been commercially rolled out with at least one major oil and gas client, enabling real-time monitoring of wellheads, pipelines, and smart meters in areas where terrestrial 5G coverage is unavailable.
A range of oil and gas companies have deployed private LTE networks, and some are now exploring or initiating upgrades to P5G. Although certain vendors promote their private LTE as being software upgradable to 5G, the transition is often more complex due to the increased technological requirements of P5G, the advanced use cases it supports, and potential differences in radio spectrum needs. As a result, some oil and gas firms face challenges in justifying private 5G upgrades at their current stage of digital transformation.
Despite the clear technical advantages of P5G, widespread adoption in the oil and gas sector has been slowed by several persistent barriers. High capital and operational expenditure requirements are significant concerns, especially as operators face ongoing cost discipline and pressure to maintain shareholder returns. The technical complexity of deploying and integrating private 5G with existing industrial systems, often across geographically dispersed and sometimes aging assets, adds further risk and delay, requiring specialist skills and careful project management. Additionally, the business case for private 5G remains difficult to quantify for many companies, with uncertain returns and a lack of clear, universal benchmarks for operational or financial benefits. These limitations are particularly pronounced for organizations with limited digital maturity or digital strategies that are focused elsewhere, making them cautious about committing to large-scale, transformative investments without proven, measurable outcomes. As a result, while leaders and early adopters are forging ahead with P5G, much of the industry is watching closely rather than accelerating deployment, waiting for clearer evidence of value before making significant commitments.
To address these challenges, the oil and gas industry should adopt a targeted approach to P5G, focusing on well-defined use cases that are contained, technically feasible, and capable of delivering short-term benefits. Collaboration across the oil and gas sector, adjacent industries, and technology partners is essential to identify shared opportunities and combine deep domain expertise with the technical capabilities of P5G and related digital or cyber-physical systems. This is particularly important in the harsh and hazardous environments typical of oil and gas operations. Building confidence and securing continued investment will depend on demonstrating tangible value through pilot projects, clear measurement of operational and financial outcomes, and transparent cost-benefit analyses.
P5G is emerging as a potential strategic enabler of digital transformation in the oil and gas sector, offering robust, low-latency connectivity for a wide range of high-value use cases, including autonomous operations and predictive maintenance, as well as enhanced safety and sustainability. Leading companies such as ADNOC, PETRONAS, Aramco, and Aker BP are demonstrating how P5G can be deployed across upstream and midstream environments to deliver measurable operational and economic benefits.
However, industry-wide adoption remains uneven. High capital costs, integration complexity, spectrum constraints, and uncertain returns on investment continue to limit broader deployment, particularly for companies with lower digital maturity or competing strategic priorities. This challenge persists even among oil and gas operators that have already deployed private LTE. While some vendors promote a straightforward upgrade path from private LTE to private 5G, the reality is more complex due to the technical demands of advanced P5G applications and the harsh environments in which they must operate.
To advance P5G adoption, oil and gas companies should be encouraged to take a focused, phased approach that prioritizes use cases that are well-understood, technically viable, and capable of delivering near-term value. Cross-sector collaboration and strong partnerships with technology providers will be key to overcoming integration barriers and aligning specialized operational knowledge with cutting-edge network capabilities. Success will depend on the ability to clearly demonstrate value through pilot deployments, supported by rigorous measurement and transparent business cases that justify continued investment.
In a sector under increasing pressure to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and reduce emissions, P5G is widely viewed as more than just a network upgrade—it is seen as a potential enabler of long-term competitiveness in a digitally driven energy landscape. While the technology holds considerable promise, realizing its full potential will depend on overcoming persistent challenges related to cost, integration, and scalability. For now, its role appears most compelling in targeted, high-value applications where the benefits can be clearly demonstrated.