

















September 2025
Manufacturing is an important sector for private 5G (P5G), with our online content survey ranking manufacturing top out of the 14 industries researched.
Ericsson, Nokia, and Verizon lead online discourse for P5G deployments in manufacturing, offering solutions for automation, robotics, digital twins, real-time analytics, and AR/VR applications. These solutions aim to improve efficiency, flexibility, safety, and enable Industry 4.0 transformation.
Diverse Global Use Cases: Leading manufacturers such as Airbus, BMW, Bosch, Ford, and Nestle are utilizing P5G for robotics, autonomous vehicles, and smart logistics, underscoring its versatility across various production environments.
Integration is a Key Hurdle: Compatibility with legacy systems and devices remains a significant challenge, often requiring substantial upgrades and meticulous system integration planning.
Security and Compliance Require Focus: While more secure than Wi-Fi, P5G introduces new risks and expands the attack surface, demanding robust cybersecurity strategies and ongoing oversight.
SMEs Face Access Gaps: Small and mid-sized manufacturers often struggle to adopt P5G due to high entry costs and limited resources, pointing to a need for more scalable and affordable deployment models.
ROI Still Mixed: Some early deployments have yet to deliver clear returns, often due to fragmented infrastructure, immature processes, or underutilized capabilities.
Partnerships Are Critical: Successful implementations usually rely on collaboration with experienced vendors and integrators to navigate technical complexity and maximize impact.
Path Forward Requires Strategic Alignment: To unlock full value, manufacturers should align P5G adoption with broader digital transformation goals, ensuring organizational readiness and selecting partners with deep integration expertise.
Industry 4.0 was introduced at the 2011 Hannover Messe international trade fair by the German government as part of its high-tech strategy to digitally transform manufacturing through the integration of advanced technologies, including IoT, AI, and cloud computing. A decade later, in the 2021 timeframe, the European Union expanded the scope to Industry 5.0, emphasizing human-centric collaboration with smart machines, resilience, and sustainability. The concepts of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 (I4.0/5.0) fall under the broader umbrella of smart manufacturing, which manufacturers have been embracing as part of their digital transformation initiatives.
Implementing I4.0/5.0 requires navigating complex technology ecosystems that span both traditional IT systems and operational technology (OT) environments. Historically siloed, IT has focused on business systems, while OT has governed production-floor cyber-physical systems. OT environments encompass a diverse array of assets, including industrial control systems (ICS), IoT/IIoT devices, robotics, and autonomous systems.
Achieving the goals of I4.0/5.0 depends on IT-OT convergence, which enables seamless data integration and automation across digital and physical domains, thereby improving efficiency, agility, and real-time decision-making. This convergence is being accelerated by the proliferation of connected cyber-physical systems, which generate increasing volumes of lateral (east-west) network traffic between IT and OT. As this traffic grows, conventional wireless solutions, such as Wi-Fi and wireless Ethernet, struggle to keep pace. In response, a growing number of manufacturers are turning to private 5G (P5G) for its superior performance, scalability, and security to support the demands of modern industrial connectivity.
Private 5G networks are rapidly becoming a valuable technology solution for modern smart factories by delivering high-speed, ultra-low-latency, and secure wireless connectivity across the production floor and supply chain. Leading manufacturers, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods, are leveraging P5G to connect thousands of sensors, autonomous robots, and logistics systems, enabling real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven quality control. This seamless machine-to-machine communication not only boosts efficiency and product quality but also enables the dynamic reconfiguration of production lines, allowing factories to adapt quickly to changing demands without requiring physical rewiring.
Beyond automation, P5G enhances worker safety and training through AR/VR applications and real-time monitoring. At the same time, it's on-premises architecture ensures critical data remains secure and compliant with strict industry standards. The deployment of private 5G is also unlocking new capabilities in digital twins, remote expert support, and precision asset tracking, further optimizing inventory management and maintenance workflows. As a result, manufacturers adopting P5G are realizing significant advancements in operational agility, scalability, and innovation, potentially positioning P5G as a foundational enabler of Industry 4.0/5.0.
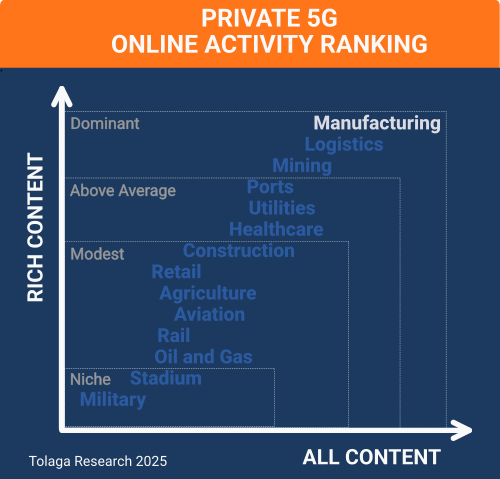
Online content published since 2022 that related to P5G in manufacturing was collected and filtered using proprietary web crawling, AI, and NLP tools, yielding a corpus of 294 relevant impressions (ALL CONTENT). Of this, 260 focused on company activity in the sector (RICH CONTENT), identifying 246 companies. Approximately 24.0 % of the content in the corpus referenced multiple industry verticals in addition to manufacturing, with an average of 2 to 3 other industries mentioned in this content.
The chart below compares the content corpus for P5G in manufacturing against other industry verticals to gauge relative market momentum. The analysis indicates that manufacturing is currently a dominant vertical market segment for P5G.
Natural language processing (NLP) and AI tools were used to identify companies mentioned in the content corpus, measure their prevalence (BREADTH), and evaluate how frequently they appear alongside other companies (DEPTH). For the 246 companies identified, the ranking of the top 10 is shown in the chart below.
Ericsson is applying P5G in manufacturing to support automation, robotics, digital twins, and real-time monitoring on factory floors. Its networks enable seamless communication between machines, sensors, and control systems, improving efficiency, safety, and flexibility compared to Wi-Fi. By supporting advanced use cases such as predictive maintenance, AR/VR-assisted operations, and AI-driven analytics, Ericsson positions P5G as a foundation for smart, data-driven manufacturing.
Nokia is deploying P5G in manufacturing through its Digital Automation Cloud and MX Industrial Edge platforms for automation, robotics, and IoT-enabled production lines. Its networks support digital twins, predictive maintenance, AR/VR applications, and real-time analytics, helping manufacturers increase efficiency, flexibility, and safety. By offering more reliable performance than Wi-Fi, Nokia positions Private 5G as a key enabler of Industry 4.0 transformation.
Verizon is deploying P5G in manufacturing by partnering with factories and technology providers to enable secure, high-capacity connectivity for automation, robotics, and IoT integration. Its networks support real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, digital twins, and AR/VR-assisted operations, improving efficiency, flexibility, and worker safety. By offering low latency and strong reliability, Verizon positions Private 5G as a foundation for modern, data-driven manufacturing environments.
NLP and AI techniques were used to identify and classify keywords and phrases in the content corpus into 22 topics. Their frequency was measured (BREADTH) and their inter-relationships analyzed (DEPTH). The chart below shows the top 10 topics.
The most prominent topics in online content today are compute and communications, artificial intelligence, industry 4.0 and 5.0, and security. Over time, we expect use-case-driven themes, such as augmented and virtual reality and agile manufacturing, to gain prominence as digital solutions continue to mature.
Manufacturers, including Airbus, BMW, Ford, Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz, Tesla, and Volvo, are deploying P5G to support robotics, autonomous vehicles, digital twins, AR/VR, and real-time analytics. Industrial firms such as BASF, Bosch, Continental, Haier, Konecranes, and Saab are using P5G for automation, predictive maintenance, quality inspection, and logistics. These deployments enhance efficiency, flexibility, safety, and transparency, but they also face challenges, including high costs, complex IT/OT integration, device compatibility issues, and limited in-house expertise. Ecosystem maturity and standardization are expected to ease barriers and support broader adoption.
Airbus is replacing traditional Wi-Fi with P5G across its global manufacturing sites, starting in France, Germany, and Spain, and then expanding to the UK, China, and the US. P5G delivers fast, reliable connectivity for tablets, smartphones, and autonomous vehicles, supporting real-time data flow, secure communications, and advanced automation. This upgrade enhances efficiency by enabling instant data capture on the factory floor, reduces manual tasks with autonomous transporters, and enhances cybersecurity by utilizing a private network. Airbus is also exploring 5G satellite links for even greater resilience and is partnering with major tech firms, such as Ericsson and Nokia. By 2028, Airbus aims to fully transition to P5G, establishing a new standard for innovative and secure aerospace manufacturing.
BASF is a global chemical company headquartered in Germany, operating in over 80 countries with a strong focus on innovation, sustainability, and serving diverse industries through products such as chemicals and plastics. The company has deployed private 5G (P5G) networks across several sites to support its digital transformation and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
At its Schwarzheide site in Lusatia, Germany, BASF has partnered with Vodafone Germany to establish a secure and independent P5G campus network. This network enables real-time communication among sensors, machines, robots, and drones, enhancing monitoring, maintenance, and overall process optimization in manufacturing.
Similarly, BASF’s facility at the Port of Antwerp in Belgium is collaborating with local provider Citymesh to deploy a 5 G network by 2025. This deployment aims to enhance worker communication, strengthen site security, and improve logistics efficiency.
In Spain, BASF deployed a P5G network in 2020 to enhance operational automation, safety, and connectivity across its large-scale chemical plants.
BMW has strategically deployed P5G networks across key manufacturing sites, including Spartanburg in the US, Dingolfing in Germany, and three facilities in China. These networks support advanced robotics, autonomous logistics vehicles, digital twin simulations, and real-time analytics, enabling precise parts tracking, instantaneous quality control, and seamless automation throughout production lines. The infrastructure also powers high-precision asset tracking and self-driving transport systems, streamlining logistics and enhancing operational transparency. Additionally, P5G enhances worker safety and training using augmented reality and real-time data overlays, while providing a scalable foundation for future Industry 4.0 technologies, including AI-driven automation and collaborative robotics.
Bosch has deployed P5G at its Salzgitter, Germany, plant in collaboration with Qualcomm Technologies and Bosch Rexroth, with a focus on integrating Qualcomm’s 5G hardware and software solutions into Bosch’s industrial automation environment. This partnership enables ultra-reliable, low-latency wireless connectivity to remotely control autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for agile quality control. The solution leverages time-sensitive networking (TSN) and coordinated multipoint (CoMP) transmission to ensure mission-critical reliability and seamless handover between antennas, while 5G precise positioning provides centimeter-level accuracy for AGV navigation.
Continental is a German multinational automotive technology company, headquartered in Hanover, Germany, and ranked as the world’s third-largest automotive supplier and a leading manufacturer of tires, brake systems, vehicle electronics, and advanced solutions for safe, efficient, and connected mobility.
Continental’s display solutions plant in Brandýs nad Labem, Czech Republic, has deployed a P5G network provided by T-Mobile Czech Republic, connecting over 1,000 devices and sensors across 5,000 square meters to drive digital transformation. This enables real-time monitoring and analytics for production optimization, predictive maintenance to reduce downtime, and seamless cross-plant collaboration. The network also supports remote maintenance using augmented reality, enabling off-site experts to assist local technicians in real-time. By leveraging T-Mobile Czech Republic’s P5G solution, Continental enhances operational efficiency, flexibility, and traceability, offering a practical blueprint for advanced Industry 4.0 adoption in automotive manufacturing, particularly in areas such as real-time analytics, remote expertise, and secure, high-density industrial IoT connectivity.
FAW Group, China’s oldest and largest automotive manufacturer, is actively implementing P5G networks to accelerate its digital transformation and smart manufacturing initiatives. In partnership with Nokia, FAW has deployed a 5G trial network at its Changchun campus to support research and development in autonomous driving, connected car applications, and industrial IoT (IIoT), enabling automation solutions such as autonomous AGVs, AR/VR machine vision, and AI-enhanced quality inspection. Additionally, FAW collaborates with ZTE to further integrate 5G, cloud computing, and edge computing into intelligent manufacturing, smart warehousing, and logistics operations.
At Ford’s historic Rouge complex in Michigan, the company deployed a private 5G industrial IoT network in partnership with AT&T in October 2021, transforming traditional manufacturing into a highly connected, data-driven operation. The network provides production line workers with real-time visibility into equipment status, inventory levels, and workflow bottlenecks, enabling them to make faster, more informed decisions directly on the factory floor. Its low-latency, high-reliability backbone supports mission-critical IoT devices, including sensors, cameras, and autonomous tools, ensuring seamless communication even in high-interference industrial environments. This integration enhances operational efficiency, enables predictive maintenance to reduce downtime, and allows agile adjustments to production schedules.
Haier, the world’s largest home appliance manufacturer, has partnered with Huawei and China Mobile to deploy a private 5G and edge computing system on its production lines. The system enables real-time, AI-driven machine vision and quality inspection through high-definition cameras and local edge servers connected via ultra-low-latency 5G. This setup enables instantaneous defect detection with over 99% accuracy, outperforming manual inspections, while also facilitating safety monitoring and workforce tracking. The architecture enhances efficiency, reduces labor costs, and serves as a scalable model for smart manufacturing that Haier is expanding across its factory network.
Hyundai has deployed P5G networks at its Ulsan Plant in South Korea—the world’s largest single-site automotive factory—and at Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA), its next-generation electric vehicle (EV) hub in Georgia, USA, which was officially opened in March 2025. These deployments deliver ultra-low-latency, high-bandwidth, and secure wireless connectivity to support industrial IoT devices, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and advanced automation systems. At Ulsan, P5G enables real-time equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of the production line. At HMGMA, the network underpins Hyundai’s vision for a fully digitalized, AI-driven EV factory, enabling seamless communication between robots, sensors, and cloud infrastructure—essential for flexible production and rapid model transitions. Hyundai’s large-scale adoption of P5G reflects a strategic move toward more resilient, data-centric, and automated manufacturing.
In April 2021, Konecranes, a global leader in material handling solutions, collaborated with Nokia and Edzcom to deploy a standalone private 5G (SA P5G) network at its Hyvinkää smart factory in Finland. The network offers ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable wireless connectivity, which is essential for real-time digital factory operations. Key applications include high-resolution wireless cameras for safer load handling and enhanced site security, enabled by the network’s ability to stream HD video with minimal delay. Beyond traditional automation, the deployment supports distributed control systems, edge computing, and digital twins, enabling real-time sensor data processing locally and instant sharing for faster, more intelligent decision-making. Building on its earlier private LTE infrastructure, Konecranes views the P5G network as a testbed for innovation in lifting technologies and automation, with the potential to extend these capabilities to customer sites worldwide.
In September 2020, Mercedes-Benz launched a private 5G network at its Factory 56 in Germany, in partnership with Telefónica and Ericsson. This deployment marked a milestone in smart manufacturing, integrating advanced robotics, automation, and real-time data analytics. The network enables seamless machine-to-machine communication, automated quality inspections, dynamic reconfiguration of production lines, and enhanced data security through on-premises processing. The implementation improved operational efficiency by up to 25% and significantly contributed to the factory’s progress toward achieving carbon-neutral production.
In 2022, Nestlé Brazil partnered with Telit Cinterion to successfully trial a P5G network at its Caçapava plant, connecting autonomous robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to enable real-time, high-reliability industrial automation. The trial demonstrated how P5G’s ultra-low latency and robust connectivity can support more flexible, efficient, and scalable smart manufacturing—a concrete step toward realizing Industry 4.0 in the food and beverage sector.
Saab, a Swedish aerospace and defense company specializing in advanced military aircraft, defense systems, and security technologies, deployed a full-scale P5G network at its aerostructures factory in Linköping during the 2020–2021 period. Implemented in partnership with Nokia and Combitech, Saab's engineering and IT consultancy, the network enables secure, real-time control of highly automated manufacturing processes, autonomous vehicle operations, and production analytics. The on-premises P5G infrastructure supports the factory’s production of critical aircraft components, including doors and wing structures for Boeing and Airbus, by providing robust machine-to-machine (M2M) connectivity, secure on-site data handling, and a foundation for Saab’s transition to Industry 4.0 and 5.0.
Tesla has successfully deployed P5G networks at its Gigafactories in Berlin and Austin, with deployment currently underway at its Shanghai facility. These networks provide ultra-reliable, low-latency wireless connectivity essential for real-time control of mobile robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and outdoor logistics systems, as well as seamless over-the-air (OTA) software updates delivered directly to vehicles on the production line. By enabling instantaneous machine-to-machine communication, P5G infrastructure supports advanced factory automation, adaptive manufacturing, and greater operational efficiency—key enablers as Tesla scales production of electric vehicles and batteries. The company's continued investment across its global factories signals its commitment to P5G as a foundational technology for its smart manufacturing strategy.
Volvo Group, in partnership with Ericsson and Airtel, is deploying a high-speed, low-latency P5G network at its Bangalore factory and R&D center to accelerate the adoption of Industry 4.0/5.0 technologies. The initiative leverages Airtel’s advanced 5G infrastructure and Ericsson’s expertise to enable real-time applications, including digital twins, extended reality (XR) for immersive training and collaboration, AI-powered analytics, and seamless human-machine interaction. By processing critical data on-premises, the project enhances both operational security and efficiency, allowing for rapid prototyping, remote diagnostics, and optimized production flows.
P5G networks in manufacturing face several key challenges, including high initial costs for infrastructure, complex integration with existing IT and OT systems, and issues with device compatibility and management. Manufacturers often lack the necessary expertise for effective deployment, struggling with scalability, interoperability, and ensuring robust security while maintaining high operational availability. Additionally, some companies have not yet realized the expected return on investment due to fragmented infrastructure, inconsistent connectivity, and limited user adoption.
The upfront costs of P5G, along with deployment complexities such as the need for spectrum licenses and specialized personnel, currently make the technology inaccessible for many manufacturers, especially small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These challenges are often compounded by IT/OT integration issues, where priorities can differ: IT typically emphasizes security, while OT must balance both availability and security.
Device compatibility presents a significant challenge for manufacturers, as most existing equipment is unlikely to support P5G at the outset of deployment. This leads to connectivity issues and complex upgrade requirements that must be addressed. Additionally, integration is often hindered by incompatibilities between P5G and legacy connectivity systems—particularly prevalent on factory floors, which further complicates adoption efforts.
Many early P5G deployments relied on highly customized solutions that lacked the modularity and scalability needed to support evolving use cases or integrate with other systems. In some instances, these implementations were over-engineered, resulting in high maintenance costs and limited flexibility for expansion. However, as the manufacturing sector matures and its requirements become clearer, solution providers are increasingly addressing these issues with more adaptable and cost-effective P5G offerings.
For many manufacturers, P5G adds another layer of operational complexity to already demanding digital transformation efforts. A lack of in-house P5G expertise often leaves organizations vulnerable to suboptimal contracts, inadequate service-level agreements (SLAs), and insufficient technical skills, which can hinder the network's ability to meet performance expectations. Moreover, some manufacturers report that P5G deployments have yet to deliver satisfactory returns on investment, citing factors such as fragmented infrastructure and limited operational maturity.
While P5G offers stronger inherent security than Wi-Fi, its deployment in manufacturing environments can introduce new vulnerabilities and expand the overall attack surface, posing additional challenges for the CISO. This expanded risk is partly due to the broader range of digital capabilities enabled by P5G, as well as specific characteristics of the technology itself. Ongoing standardization efforts by organizations like 3GPP are helping to address these unique security concerns, which are expected to ease some of the burden on security teams over time.
P5G is emerging as a transformative enabler for smart manufacturing, offering the performance, reliability, and security needed to realize the full potential of Industry 4.0 and 5.0. As illustrated by leading manufacturers worldwide, P5G supports a wide range of advanced use cases—from autonomous logistics and real-time analytics to digital twins and machine vision—helping to drive innovation, efficiency, and agility on the factory floor.
However, widespread adoption remains uneven, constrained by high upfront costs, integration challenges, and gaps in in-house expertise. Early implementations often suffered from scalability and interoperability issues, and some deployments have yet to deliver the anticipated return on investment. Despite these obstacles, the technology is evolving rapidly. Ecosystem maturity, improved standardization, and the emergence of more modular, cost-effective solutions are helping to address critical barriers.
For manufacturers, the path forward lies in aligning P5G adoption with broader digital transformation strategies, ensuring technical readiness, and partnering with experienced solution providers. With the right foundations in place, P5G can serve as a key catalyst for the next generation of resilient, intelligent, and human-centric manufacturing.