

















September 2025
Construction is a modest opportunity for Private 5G (P5G), with our online content survey ranking construction 7th out of the 14 industries researched.
Ericsson, Samsung, Nokia, Huawei, and NTT are most visible in online content relating to P5G for construction, providing secure, low-latency connectivity that supports automation, robotics, IoT sensors, real-time monitoring, safety systems, and centralized management to improve site efficiency and productivity.
The construction industry is undergoing digital transformation, leveraging technologies like BIM, IoT, AI, and AR/VR to improve efficiency, safety, and collaboration. Reliable wireless connectivity is a critical enabler, particularly on large, complex, or remote sites where wired infrastructure is often impractical.
P5G is seeing growing interest for its potential to support real-time monitoring, automation, and remote operations. However, current deployments remain limited, and the technology’s cost, complexity, and integration demands hinder widespread adoption.
Use cases from projects such as Merck’s Bio Manufacturing Center, the Silvertown Tunnel, and Hoban Construction highlight the promise of P5G in enabling AI-powered safety systems, real-time data capture, and enhanced digital workflows. Still, these remain the exception rather than the norm.
Key challenges include high upfront investment, spectrum access, device compatibility, and a shortage of internal expertise. These are being addressed through modular "5G-in-a-box" solutions, partnerships with experienced providers, and hybrid network solutions that combine P5G with existing wireless technologies.
While P5G holds promise for the construction industry, it is not yet a mainstream solution. Adoption is likely to remain limited until its costs and complexities are reduced, and its value compared to alternatives like Wi-Fi and public 4G or 5G is more clearly demonstrated. A phased approach based on specific use cases, supported by pilot projects and ongoing evaluation, will be critical to understanding its long-term role in the industry's digital transformation.
The construction industry is adopting digital technologies with the goal of enhancing productivity, reducing costs, improving communication, and addressing labor shortages through real-time collaboration, automation, data-driven insights, and project transparency.
Key technologies include Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems from providers such as Autodesk, Bentley Systems, Nemetschek, Trimble, and Hexagon AB. These systems are increasingly integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enable predictive analytics and automate workflows. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors provide real-time monitoring of equipment and environmental conditions, while cloud platforms facilitate seamless data sharing and remote collaboration. In addition, emerging innovations, including digital twins, augmented and virtual reality, robotics, drones, and 3D printing, are also being adopted for simulation, training, site surveying, and on-site fabrication.
Although the industry has traditionally lagged in digital adoption, momentum is growing, and these technologies are the foundation of integrated digital ecosystems that are reshaping the construction landscape.
Wireless connectivity is essential to enabling these ecosystems, particularly across large, dynamic, and often remote sites where wired infrastructure is impractical. Several options are available, including public 4G/5G networks, Wi-Fi, and Private 5G (P5G), each with distinct trade-offs. P5G offers superior reliability, low latency, and robust security, making it well-suited for high-density, mobile construction environments; however, it comes with higher upfront costs and increased integration complexity. Public 4G/5G networks offer broad coverage and mobility at a lower initial cost but provide less control and variable performance. Wi-Fi remains a cost-effective choice for static indoor areas; however, it is limited in terms of mobility, outdoor coverage, and resilience to interference.
P5G is enabling advanced digital applications that enhance safety, productivity, and operational efficiency across various sites and project types. Key use cases include real-time CCTV surveillance, AI-driven hazard detection, and the use of smart wearables for worker health and safety, as seen in Merck’s bioprocessing facility project in South Korea. Projects like the Silvertown Tunnel in London and the Shetland HVDC station demonstrate how P5G supports secure communications, remote collaboration, AR/VR, drone operations, and environmental monitoring. Gammon Construction, Hoban, and Ferrovial have deployed P5G to enable robotics, concrete curing sensors, and smart safety gear. At the same time, NTT and Karta-X Technologies showcase high-resolution AI safety systems on millimeter-wave spectrum. Telstra's Melbourne site illustrates how private 5G with network slicing accelerates deployment and enables remote machine operations. Portable solutions, such as T-Mobile’s “5G On Demand,” bring flexibility and rapid deployment to temporary or remote sites. Across all cases, P5G delivers the low-latency, high-bandwidth, and reliable connectivity needed to support digital workflows, improve decision-making, and future-proof construction operations.
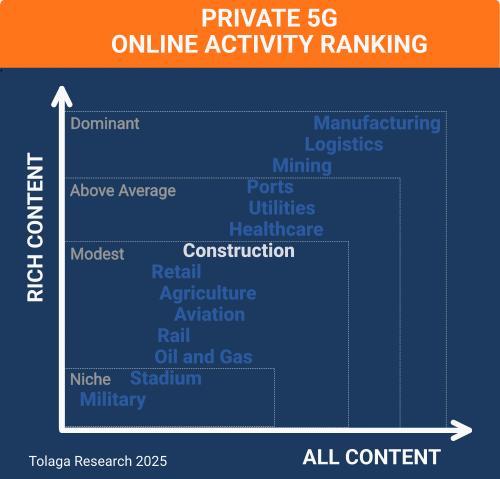
Online content published since 2022 that related to P5G in construction was collected and filtered using proprietary web crawling, AI, and NLP tools, yielding a corpus of 163 relevant impressions (ALL CONTENT). Of this, 127 focused on company activity in the sector (RICH CONTENT), identifying 94 companies. Approximately 23.0 % of the content in the corpus referenced multiple industry verticals in addition to construction, with an average of 2 to 3 industries mentioned in this content.
The chart below compares the content corpus for P5G in construction against other industry verticals to gauge relative market momentum. The analysis indicates that P5G has shown only modest momentum in construction compared with other sectors.
Natural language processing (NLP) and AI tools were used to identify companies mentioned in the content corpus, measure their prevalence (BREADTH), and evaluate how frequently they appear alongside other companies (DEPTH). Of the 94 companies identified, the ranking of the top 10 is shown in the chart below.
Ericsson is using P5G in construction to deliver secure, high-performance connectivity that supports automation, remote machine operation, and real-time monitoring. Its dedicated networks replace patchy Wi-Fi, improve safety, reduce downtime, and enable smarter, more efficient worksites.
Nokia is advancing P5G in construction through its Digital Automation Cloud and MX Industrial Edge platforms, enabling reliable connectivity for automation, IoT sensors, robotics, video monitoring, and connected workers. It also offers compact solutions for smaller sites, improving safety, efficiency, and deployment flexibility compared to Wi-Fi.
Samsung is applying P5G in construction through partnerships such as with NAVER Cloud at Hoban Construction in Korea. Its networks enable drone-based monitoring, IoT concrete sensors, smart safety wearables, and real-time video feeds, helping firms track progress, enhance safety, and improve site efficiency.
Huawei is bringing P5G to construction and related industries by supporting augmented reality training, video analytics, IoT sensors, and remote equipment monitoring. Its approach emphasizes dedicated spectrum, edge computing, and low latency to enhance safety, automation, and overall operational performance.
NTT offers P5G solutions in construction to enhance safety and efficiency through AI-powered video, sensors, and edge computing. Projects such as a Hong Kong landfill site use private 5G cameras to detect hazards in real-time, while its CROSS LAB initiative supports new IoT and AR/AI use cases for construction firms.
NLP and AI techniques were used to identify and classify keywords and phrases in the content corpus into 16 topics. Their frequency was measured (BREADTH) and their inter-relationships analyzed (DEPTH). The chart below shows the top 10 topics.
The prominent topics in online content today are compute and communications, construction, and security. Looking ahead, we expect areas such as artificial intelligence, asset management, workforce, wearables, and augmented and virtual reality to gain prominence as digitally enabled solutions continue to mature.
P5G is being deployed across construction projects worldwide to deliver secure, low-latency connectivity for applications including CCTV, hazard detection, IoT sensors, robotics, drones, and AR/VR. The goal is to enhance safety, productivity, and operational efficiency. Key adoption challenges include high costs, technical complexity, regulatory requirements, and integration with existing systems, though solutions such as Open RAN, modular architectures, and portable 5G-in-a-box deployments are helping to mitigate these barriers. Several notable examples are summarized below.
In March 2024, Merck launched construction of a USD 325 million bioprocessing facility in Daejeon, South Korea, awarding the build to Kolon Global. As part of the project, Kolon Global partnered with HFR Mobile to deploy a P5G network, enabling real-time high-definition CCTV surveillance, AI-driven hazard detection, and smart wearables for worker health and safety monitoring. The integrated system provides instant alerts and automated emergency responses, enhancing on-site safety and operational efficiency.
The Silvertown Tunnel Project involves the construction of a new twin-bore road tunnel beneath the River Thames, connecting Silvertown in Newham to the Greenwich Peninsula. In October 2021, Ferrovial, a leading contractor on the project, partnered with Nokia and Telent to deploy the United Kingdom’s first operational 5G standalone (SA) private wireless network at the construction site. The network uses Nokia’s Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) and operates on Ofcom’s shared spectrum in the 3.3–4.7 GHz band. Telent provided systems integration services for the deployment and now operates the network, while Neutroon delivers cloud-based management and orchestration. The network enables real-time communication, advanced security, access control, and environmental monitoring, enhancing health and safety and improving overall operational efficiency.
The Shetland HVDC converter station project was launched in 2020 to establish the first direct connection between Shetland and the United Kingdom’s electricity grid. BAM Nuttall led the civil engineering works and took a pioneering step by deploying a private 5G network based on Open RAN (ORAN) technology. The network featured core infrastructure from Attacore, a UK-based start-up, along with radio access technology from another UK RAN provider. This high-performance network enabled real-time collaboration using digital cameras, drones, augmented and virtual reality, and IoT sensors—allowing remote teams to monitor progress and make informed decisions without being on-site. It also supported automation and robotics capabilities, including Boston Dynamics solutions for remote surveying, inspection, and safety monitoring, enhancing both productivity and site safety.
Gammon Construction is a leading construction and engineering firm headquartered in Hong Kong, with a strong presence across China and Southeast Asia. To enhance its operations, Gammon partnered with Singtel to deploy campus-based wireless networks that use network slicing to deliver tailored private 5G (P5G) solutions. These networks support advanced use cases on construction sites, including robotics, CCTV, drone inspections, and augmented reality.
Accenture is collaborating with Virgin Media O2 (VMO2) to deliver private 5G solutions tailored to the UK construction industry as part of a broader push into the mobile private network market. Their joint offering is built on Accenture’s Edge Orchestration Platform and integrates edge computing, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded cybersecurity—technologies designed to meet the unique connectivity and digital transformation needs of construction sites.
In October 2022,Cellnex and Ferrovial announced a partnership aimed at advancing private 5G adoption in the construction industry. The collaboration focuses on delivering flexible private 5G solutions based on Open RAN architecture. These networks are designed to connect a wide range of devices on construction sites—including IoT sensors, augmented reality tools, AI systems, and robotics from multiple vendors—enabling diverse user groups and supporting advanced digital workflows.
In November 2022, Hoban, a leading construction company in South Korea, deployed a dedicated private 5G network at a large-scale apartment project in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and NAVER Cloud. Operating in the 4.7–4.8 GHz band reserved for private 5G in Korea, the network supported a range of advanced capabilities, including real-time drone inspections, IoT sensors for monitoring concrete curing, smart safety jackets equipped with emergency features (e.g. gas detection, cameras, and emergency buttons) and cameras, wireless 4K CCTV surveillance, and seamless digital collaboration tools.
In January 2025, Karta-X Technologies and NTT launched a pilot project at a landfill construction site in Hong Kong, demonstrating the integration of Karta-X’s AI cameras and computer vision platform with NTT’s private 5G network to enhance safety through real-time hazard detection. Operating in the 26–28 GHz millimeter-wave spectrum, the P5G network delivers the ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and reliable coverage required to support advanced AI applications in complex outdoor construction environments, where traditional Wi-Fi and 4G connectivity often fail to meet the requirements.
In February 2023, Telstra demonstrated its private 5G network slicing solution at a construction site in Melbourne. The network provided guaranteed bandwidth and low latency for critical applications such as CCTV, collaboration, and data transfer—allowing the site to become operational months earlier than would have been possible with traditional fixed-line infrastructure. The solution, built on Ericsson-Cradlepoint 5G technology, supported a range of advanced use cases, including augmented and virtual reality, real-time data visualization, remote machine operation, and embedded IoT sensors for progress tracking.
Several mobile network operators, including Verizon and T-Mobile, have announced P5G solutions targeted for the construction industry. For example, in September 2023, T-Mobile announced “5G On Demand,” a portable private 5G network-in-a-box solution designed for rapid deployment at construction sites. Powered by Ericsson technology, the solution can be deployed in under 48 hours, even in remote or challenging environments, and includes setup, teardown, and full network management. T-Mobile positions the solution to deliver cost savings, operational flexibility, and support for advanced digital workflows, while improving safety and productivity in dynamic, temporary, or hard-to-reach environments through next-generation wireless connectivity.
In September 2024, Xingtera announced a partnership with Celona to deliver P5G in China to various industries, including construction. The partnership leverages Celona’s P5G platform, radio spectrum from Oriental Cable Network, and core and edge server infrastructure from Inspur.
P5G networks offer construction companies the potential for real-time monitoring, automation, and improved safety; however, adoption faces challenges, including high costs for spectrum and infrastructure, technical complexity, a shortage of in-house expertise, device compatibility issues, and difficulties achieving seamless coverage and mobility across dynamic sites. Regulatory hurdles and the need to integrate with existing systems add further complexity. These challenges can be addressed by partnering with experienced systems integrators and wireless infrastructure technology providers, leveraging shared or lightly licensed spectrum, adopting modular and interoperable solutions (e.g., 5G-in-a-box and ORAN), and implementing hybrid networks that combine private 5G with Wi-Fi and public cellular for greater flexibility. Focusing on high-value use cases, engaging with regulators, and investing in training can also help ease adoption challenges, enabling construction firms to harness the benefits of P5G while mitigating its risks.
The construction industry’s growing adoption of digital technologies is increasingly supported by advanced wireless connectivity, with P5G emerging as one of several viable options. Case studies from projects in South Korea, the UK, Australia, Hong Kong, and elsewhere demonstrate that P5G can enable real-time monitoring, automation, and enhanced collaboration on large or complex sites. These deployments have shown potential benefits in areas such as safety, operational efficiency, and data-driven decision-making, often integrating with other digital tools, including IoT sensors, AI analytics, and augmented reality.
However, the practical implementation of P5G faces notable challenges. High initial costs, technical complexity, regulatory requirements, and the need for specialized expertise can limit uptake, particularly for smaller firms or less capital-intensive projects. In response, some organizations are exploring hybrid network approaches, modular solutions, and partnerships with technology providers to reduce barriers and improve flexibility.
While P5G is not yet a mainstream solution, its role in supporting the construction industry’s digital transformation is becoming clearer. The extent to which it will be widely adopted depends on continued technological evolution, cost reductions, and the ability to address integration and operational challenges. For now, P5G represents one part of a broader shift toward more connected, data-driven construction practices, with its ultimate impact still to be determined by real-world experience and further innovation.
To realize the potential of P5G in construction, firms should start by identifying high-impact use cases—such as safety monitoring, automation, and remote collaboration—where P5G offers clear advantages over existing networks. A phased, pilot-first approach allows organizations to validate value before scaling. Hybrid network architectures that combine P5G with Wi-Fi and public cellular can improve flexibility and coverage while controlling costs.
Partnering with experienced integrators and adopting modular solutions like “5G-in-a-box” can simplify deployment, particularly on remote or temporary sites. Engaging with regulators to secure spectrum access (or mobile operators to secure network slices) and investing in workforce training will help address adoption barriers. In addition, measuring performance and sharing best practices across the industry will accelerate adoption and support the broader digital transformation of the construction sector.