

















September 2025
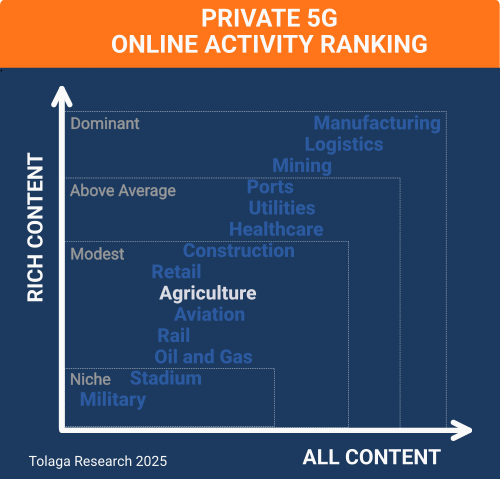
Agriculture is a modest opportunity for Private 5G (P5G), with our online content survey ranking agriculture 9th out of the 14 industries researched.
Ericsson and Nokia feature most prominently online, supporting early industry adopters with solutions that drive automation, real-time monitoring, and digitalization, with a strong focus on operational efficiency and sustainability.
P5G can enable smarter, more connected agriculture, offering secure, high-speed connectivity for real-time data, IoT devices, automation, and AI-powered insights, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Most deployments are still pilot projects, supported by public funding or large industry partnerships. Full-scale commercial adoption remains limited, reflecting the technology’s early maturity in agriculture.
Use cases are varied and promising, including autonomous machinery, crop and livestock monitoring, predictive maintenance, and smart irrigation. Reported benefits include improved yields, efficiency, and sustainability.
Key barriers persist, including high costs, technical complexity, and a lack of on-farm IT expertise—particularly for small and mid-sized producers.
Collaborative ecosystems are critical, helping to reduce risk and accelerate innovation through public-private partnerships, research hubs, and open innovation platforms.
Wider adoption will require clear ROI and scalable models, tailored to specific farming contexts and integrated with existing agricultural systems.
Digital agriculture and smart-farming initiatives encompass a diverse range of technologies and programs aimed at enhancing productivity, sustainability, and resilience throughout the agricultural value chain. These efforts leverage data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), remote sensing, drone surveillance, digital twins, and, in some cases, blockchain technologies to generate insights, automate processes, and support better decision-making by farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers. Many of these technologies require robust wireless connectivity, which can be delivered through a range of options, including LoRa/LoRaWAN, Bluetooth, RFID, Wi-Fi, public 4G/5G, satellite, and private 5G (P5G) networks.
P5G offers a distinct value proposition for smart agriculture, delivering secure, high-speed, low-latency, and reliable connectivity to rural and remote areas, capabilities that traditional infrastructure often lacks. These features enable real-time monitoring, automate farm machinery, and integrate advanced analytics with edge computing at the farm level. Despite this potential to support the transformation of agriculture into a more connected, data-driven industry, P5G adoption remains tentative. Most current deployments are still experimental and pilot-based, typically either funded by public or consortium sources or limited to large-scale, well-resourced farms in regions with supportive policy environments. Significant barriers to broader adoption include high implementation costs, technical complexity, and a shortage of IT expertise, with the economic benefits of large-scale P5G deployments in agriculture yet to be clearly demonstrated.
P5G in agriculture is enabling a wide range of advanced, data-driven use cases across diverse geographies and farm types. Common applications include real-time monitoring of crops, livestock, and environmental conditions using IoT sensors, drones, and AI-powered analytics. These systems support precision agriculture through automated irrigation, pest control, fertilization, and disease detection, leading to higher yields, reduced chemical usage, and improved sustainability. P5G also facilitates fully autonomous farming operations, including plowing, planting, harvesting, and robotic inventory or livestock management, often replacing hazardous or labor-intensive tasks. In livestock settings, it enables continuous health monitoring, early anomaly detection, and remote care via telemedicine. Many deployments also integrate edge computing and cloud platforms to streamline data collection, automate decision-making, and support digital twins for predictive maintenance. Additionally, P5G supports broader farm operations such as predictive maintenance of machinery, asset tracking, enhanced food safety, and agritourism services. These real-world pilots collectively demonstrate how P5G can transform agricultural productivity, environmental stewardship, and rural connectivity, while also serving as innovation platforms for scalable smart farming solutions.
Online content published since 2022 that related to P5G in agriculture was collected and filtered using proprietary web crawling, AI, and NLP tools, yielding a corpus of 140 relevant impressions (ALL CONTENT). Of this, 103 focused on company activity in the sector (RICH CONTENT), identifying 84 companies. Approximately 22.0 percent of the content in the corpus referenced multiple industry verticals in addition to agriculture, with an average of 2 to 3 industries mentioned in this content.
The chart opposite compares the content corpus for P5G in agriculture against other industry verticals to gauge relative market momentum. The analysis indicates that P5G has shown only modest momentum in agriculture compared with other sectors.
Natural language processing (NLP) and AI tools were used to identify companies mentioned in the content corpus, measure their prevalence (BREADTH), and evaluate how frequently they appear alongside other companies (DEPTH). Of the 84 companies identified, the ranking of the top 10 is shown in the chart below.
Ericsson is actively working with partners and research programs to deploy 5G Standalone (SA) networks in rural and farming settings for key use-cases, including precision agriculture and closing digital divides. For example, Ericsson helped build a private 5G SA network in Iowa through a National Science Foundation (NSF) program, covering crop and livestock farms and enabling use cases such as plant-phenotyping robots, livestock monitoring via high-resolution cameras, and the automation of farming operations. In Australia, Ericsson has partnered with AgriBusiness Connect (and Telstra) to roll out private 5G infrastructure at an agri-technology hub (AATLIS in Toowoomba), targeting things like machinery monitoring, predictive maintenance, supply chain logistics, and boosting digitalization of the agricultural sector.
Nokia is collaborating with partners in Latin America and other regions to deploy P5G networks that address the connectivity challenges of agriculture. For example, in Brazil, it has teamed with Solis to deliver private networks for farms, enabling real-time monitoring of machinery, crops, and resources through IoT sensors and cloud platforms. More broadly, Nokia is extending rural connectivity through base stations and small cells designed for remote farm environments, aiming to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and food production by supporting precision farming tools, worker communications, and advanced analytics.
NLP and AI techniques were used to identify and classify keywords and phrases in the content corpus into 14 topics. Their frequency was measured (BREADTH) and their inter-relationships analyzed (DEPTH). The chart below shows the top 10 topics.
The most prominent topics in online content are currently compute and communications, precision agriculture, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Since P5G in agriculture is still at an early stage, the strong presence of compute and communications is expected. Over time, the focus is likely to shift from enabling technologies such as compute, connectivity, and IoT toward service-level capabilities, including precision agriculture, AI, robotics, and AR/VR.
P5G has been applied across diverse agricultural use cases, enabling capabilities such as automation, real-time environmental and condition monitoring, and data-driven decision-making. Key complementary technologies include IoT and sensor networks, drones, and AI. Many of these applications are supported by government initiatives and are designed to increase productivity, enhance crop and livestock yields, and promote sustainable farming practices. Several notable use cases are summarized below.
The RuralDorset 5G Project, led by Dorset Council, explored how P5G could improve rural services—including agriculture, public safety, and coastal monitoring—through real-world trials in remote and hard-to-reach areas.
Running from March 2020 to September 2022, the project piloted a variety of agricultural and aquacultural use cases, such as drone- and IoT-enabled crop monitoring, autonomous weeding robots, livestock health tracking using P5G-powered computer vision, and real-time sensor systems for fish farms and environmental monitoring. These demonstrations highlighted the potential of 5G and IoT to support more precise, automated, and sustainable food production while enabling data-driven decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Qualcomm contributed to the project by testing mmWave 5G technology, including the 26 GHz band, for advanced agricultural applications. This included precision per-plant farming, drone-based field surveillance, and weed removal using electric robots, demonstrating potential yield increases of up to 200% and significant reductions in pesticide use.
The Growing Sussex 5G Innovation Region is a West Sussex County Council-led initiative launched in November 2023 with £3.8 million in funding from the UK’s Department for Science, Innovation and Technology. It brings together growers, educators, and technology providers to trial advanced technologies that support sustainable food and drink production. Key partners include East Sussex County Council, the West Sussex Growers Association, Wicks Farm, The Green House Sussex Ltd, Boldyn Networks, Archipelagos Labs, and academic institutions such as the University of Brighton, Plumpton College, and Brinsbury College. The collaboration aims to integrate P5G, AI, and IoT into agriculture and viticulture, build digital skills, and develop scalable, commercially viable solutions for the region.
Scotland’s National Robotarium Consortium is a strategic partnership—led by Heriot‑Watt University in collaboration with the University of Edinburgh and backed by the Edinburgh & South‑East Scotland City Region Deal, focused on advancing world-class robotics and AI research, innovation, and industry collaboration from its state‑of‑the‑art £22.4 million facility in Edinburgh. In collaboration with Freshwave and Boston Dynamics, it is leveraging private, portable 5G networks to develop and demonstrate advanced robotics for precision agriculture. Their focus is on testing real-world deployments of 5G-connected agricultural robots, such as Boston Dynamics’ “Spot,” to perform tasks like crop health monitoring, soil condition assessment, targeted fertilizer application, and early detection of diseases and pests.
The Hefeng Unmanned Farm in Zibo, Shandong, is a flagship Chinese demonstration project covering approximately 33 hectares. It was jointly established by Shandong University of Technology and Zibo Hefeng Seed, a seed production company, with technology and services provided by Huawei and China Mobile. The project combines 5G, IoT, satellite remote sensing, and automated machinery to enable fully autonomous plowing, planting, crop management, and harvesting. The project aims to illustrate how advanced digital technologies can support large-scale, efficient, and sustainable modern agriculture.
SLC Agrícola is Brazil’s largest publicly traded agribusiness company, specializing in large-scale, technology-driven crop production, including soybeans, corn, and cotton. It partnered with Claro, Embratel and Huawei to pilot P5G Standalone (SA) networks in an experimental 3.5GHz spectrum license provided by Brazil’s regulator Anatel, on its farms, focusing on advanced applications enabled by real-time data. The pilot demonstrated practical benefits of P5G SA, including the rapid transmission of high-resolution field images, integration of sensors and drones, and AI-driven automation, which collectively improved operational efficiency, sustainability, and the speed of response to pests and other threats.
AgriBusiness Connect (a not-for-profit joint initiative of FKG Group, the University of Queensland, and Telstra) is an Australian innovation hub that brings together primary producers, manufacturers, researchers, and government to drive the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies. In January 2022, it partnered with Telstra to deploy an Ericsson P5G network at its Toowoomba site. The network supports real-time data collection from farm machinery and sensors, enabling applications such as asset condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automation. This enhanced operational efficiency, reduced unplanned downtime, and aimed to provide a foundation for scaling smart farming and manufacturing technologies across Australia’s agricultural sector.
In 2024, systems integrator Invences partnered with Trilogy Networks—specialists in software, cloud, and edge platforms—to deploy P5G networks tailored for large-scale agriculture, with a flagship pilot in Fargo, North Dakota. The solution was designed to overcome key barriers in modern farming, including poor rural connectivity, fragmented technologies, and complex system integration. By delivering high-speed, low-latency, and secure wireless infrastructure, the deployment enabled real-time data collection from IoT sensors monitoring soil moisture, crop health, weather conditions, and livestock. These sensors, along with drones and edge devices, were connected to cloud-based AI analytics platforms that provided actionable insights through mobile and web apps for irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. The system reduced labor costs by up to 20% and water and fertilizer use by as much as 25%. Overall, the pilot achieved a 20–30% increase in crop yields, highlighting the transformative impact of P5G on agricultural productivity, sustainability, and efficiency.
Ushino Nakayama's Osumi Farm in Kanoya, Kagoshima, Japan, spans approximately 30 hectares and houses 5,000 Japanese Black (Wagyu) cattle across 42 barns. The farm is leveraging P5G to develop an advanced smart farming system, focusing on enhancing productivity and animal welfare through automation and real-time analytics.
The P5G network delivers the high-speed, low-latency connectivity required to support 4K ceiling-mounted cameras in each cattle cell, paired with AI-powered image analysis. This setup enables continuous monitoring of individual cattle health and behavior. If abnormalities are detected, such as an animal struggling to stand, the system issues alerts and can deploy self-propelled robots equipped with high-resolution cameras for close-up inspection, all managed remotely in real-time.
This technology has already helped Osumi Farm reduce labor costs by more than 10%, lower accident rates, and minimize feed and administrative losses. It also supports remote work, helping address labor shortages.
Beyond immediate gains, the system collects detailed, real-time data on each animal, supporting precision livestock farming and the farm's ambitious goal of achieving “zero mortality” during the fattening process. This data could eventually be used to predict meat quality, enable direct-to-consumer business models, and redefine best practices in livestock management both in Japan and globally.
While challenges remain—technical, economic, and cultural, Osumi Farm's integration of ICT with traditional livestock practices represents a compelling blueprint for the future of digital agriculture.
ZTE and China Mobile have transformed 12,000 acres of saline-alkali land near Da’an City in Jilin Province into China’s first fully automated P5G rice farm, showcasing how advanced connectivity can revitalize previously unproductive terrain.
Through the deployment of a standalone P5G network, the farm supports remote-controlled machinery, smart irrigation systems, and drone-based monitoring—enabling full-cycle rice production with minimal human intervention. Since its launch as a pilot in 2021, the project has increased crop yields by 10%, reduced water consumption by 40%, and delivered substantial labor and cost savings.
The success of the initiative has proven the economic and environmental viability of P5G-powered smart farming, offering a scalable model for sustainable agriculture in some of China’s most challenging landscapes.
Deutsche Telekom’s Smarter Weinberg (Smart Vineyard) project was announced in September 2024 as a dedicated 5 G campus network in the Moselle Valley, Germany, to modernize a long-time wine-growing region plagued by labor shortages and rugged terrain. By equipping the vineyard with autonomous, 5G-connected robots and AI-powered analytics for real-time data on vine health and environmental conditions, the initiative enables precision farming, optimizes water and pesticide use, and allows for the remote control of agricultural machinery via edge cloud technology. The project also serves as a testbed for studying 5G signal propagation in challenging, rural environments. Developed in partnership with academic institutions and local growers, Smarter Weinberg aims to preserve traditional viticulture through sustainable, automated solutions, demonstrating how advanced connectivity and digital tools can future-proof agriculture in steep and remote landscapes.
The 5G AgriTech Innovation Hub (5G MPN Hub) was established in 2023 under the leadership of Vodafone Hungary. Research is conducted at the hub to enable advanced IoT use cases, including real-time machine-to-machine connections and automated weed monitoring, which aim to increase crop yield, reduce costs, and support the transition to sustainable food systems. The network will offer high-speed, low-latency connectivity (peak 1200/120 Mbps, <10ms latency), leveraging massive MIMO and edge cloud services for real-time, secure data processing. After its initial validation, the hub serves as an open-source innovation space, inviting universities, SMEs, and startups to co-create and scale solutions, with the goal of accelerating digital adoption across EU agriculture.
Swan Trails Farm in Snohomish, Washington, is a historic, family-run farm and agritourism destination renowned for its seasonal attractions, including a well-known corn maze, pumpkin patch, and event spaces, all set along the scenic Snohomish River.
In October 2024, MosoLabs and KhasmX deployed a P5G network at the 80-acre farm using their turnkey KhasmX+MosoLabs P5G Kit. The solution, leveraging CBRS spectrum and MosoLabs’ Canopy 5G radios, delivered enterprise-grade connectivity across the entire site, including areas lacking traditional broadband access.
The network supports critical operations, including point-of-sale systems, staff communications, and guest safety, vital for accommodating up to 20,000 visitors per week during peak events. It also enables on-site edge computing and AI workloads, integrates seamlessly with existing IT systems, and is designed for ease of deployment, reducing the need for deep technical expertise.
The 5G4AGRI project is a collaborative initiative led by the Pays de la Loire Chamber of Agriculture in France, supported by Orange 5G Lab and Orange Business, along with a consortium of companies, academic institutions, and research organizations.
At the Derval farm, P5G connectivity enables applications such as agricultural robotics, AI-powered livestock monitoring, remote surveillance, and veterinary telemedicine. The project also partners with the Nantes Veterinary School and telemedicine startup AMA to explore digital health solutions for animals.
Orange contributes its 5G technical expertise to support secure, high-performance connectivity, enabling real-time data transfer and powering innovative agricultural use cases across both sites. The project aims to demonstrate how P5G can accelerate the digital transformation of livestock and crop production through reliable, scalable solutions.
Hofgut Neumühle is a teaching and experimental research farm in Germany, focusing on livestock husbandry, dairy production, and sustainable agriculture. It serves as a hub where applied research, digital innovation, and hands-on education converge to promote animal welfare, resource efficiency, and knowledge transfer in modern farming.
The farm is integrated into a pioneering P5G standalone (SA) campus network deployed across Technische Universität Kaiserslautern (TUK) and its affiliated research facilities. Supplied by Nokia and implemented by Smart Mobile Labs AG, the network delivers industrial-grade, high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity tailored for research and real-world testing in sectors such as agriculture, logistics, and construction.
Funded by the German Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure under the 5G-Kaiserslautern initiative, the project provides a controlled environment for exploring advanced 5G applications—including autonomous vehicles, drone operations, real-time video analytics, and IoT-driven farm management.
By incorporating Hofgut Neumühle into this ecosystem, the project transforms the farm into a living lab for precision agriculture, enabling the development and demonstration of more innovative, more connected, and efficient farming practices.
Overbury Farms is a large, family-owned arable and sheep farm spanning approximately 3,800 acres on the Worcestershire–Gloucestershire border in the Cotswolds. It is at the forefront of P5G adoption in UK agriculture, through a portable, scalable network deployed in partnership with Virgin Media O2 Business (VMO2) and the River Severn Partnership Advanced Wireless Innovation Region (RSPAWIR).
Launched in early 2025, the deployment covers a 0.4-square-mile trial area on the estate, using elevated grain storage facilities for antenna placement to extend coverage up to 0.8 square miles north and 0.4 square miles south—far beyond the reach of traditional rural Wi-Fi networks. The carrier-grade P5G network supports advanced agricultural applications, including AI-driven pest monitoring, real-time environmental sensors (for water quality, soil moisture, and weather), IoT-enabled livestock management, and seamless data collection and analytics.
A GBP 3.75 million government grant supports the project as a national showcase for addressing rural connectivity challenges. It aims to improve farm efficiency, animal welfare, and environmental monitoring, while demonstrating how P5G can work in conjunction with existing digital farming tools, such as connected tractors and weather stations.
The Food Resiliency Project in Washington State is a USD 7.3 million initiative supported by federal and state partnerships aimed at strengthening local and regional food supply chains. It focuses on expanding infrastructure for processing, storage, and distribution—especially for small and underserved producers—by modernizing equipment, improving food safety, and increasing market access. The project was launched in response to the disruptions in the food system experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic and is designed to build a more resilient, equitable, and stable food supply across the state.
A key component of the project is the integration of P5G networks at two operational farms—Swans Trail Farms and Andrews Hay. Designed and deployed by Ballast Networks, with Microsoft providing cloud and edge platforms and Nokia supplying network infrastructure, the P5G connectivity enables real-time data collection and analysis essential for modern agriculture. Farmers can leverage IoT devices, edge computing, and cloud analytics to monitor irrigation, soil conditions, labor use, and resource efficiency—driving improvements in yield, sustainability, and operational performance.
The initiative is further supported by technology partners, including Intel, T-Mobile, and VMware, all of which are coordinated through the 5G Open Innovation Lab. This collaborative platform brings together developers, enterprises, government, and academic institutions to co-create and test next-generation agricultural technology (AgTech) solutions.
By embedding advanced connectivity and analytics into farming operations, the Food Resiliency Project empowers local producers with actionable insights and automation tools, while serving as a replicable model for building technology-driven food system resilience.
P5G presents a potentially promising yet emerging pathway for advancing digital agriculture. Its ability to deliver secure, high-speed, and low-latency connectivity makes it well suited for enabling technologies such as IoT sensors, autonomous equipment, and AI-driven analytics—particularly in rural areas where traditional connectivity is limited. The case studies examined in this report showcase a diverse range of innovative use cases, from precision livestock farming in Japan to fully automated rice production in China and smart viticulture in Germany. These early deployments demonstrate tangible benefits in productivity, efficiency, and sustainability, while also serving as valuable testbeds for refining AgTech solutions.
At the same time, P5G adoption in agriculture remains at a formative stage. Most projects are pilots or publicly supported demonstrations, with deployment often limited to larger farms or innovation hubs with access to funding, technical expertise, and supportive policy environments. High capital costs, integration challenges, and the need for specialized skills remain significant barriers to broader uptake—particularly among small and mid-sized farms. Moving forward, efforts to simplify deployment, build local capacity, and clearly demonstrate return on investment will be critical to unlocking the full potential of P5G. If these challenges are addressed, P5G could become a foundational enabler of more connected, data-driven, and resilient agricultural systems.